Have you ever wondered what makes your computer stay cool, or how your telecom equipment can work flawlessly in hot environments? Well, my friends, today we’re pulling back the curtain on a secret superhero in the world of electronics: the thermal compound. In this article, we’ll explore what thermal compound is, what it’s made of, and how it can work wonders for different applications, far beyond just keeping your PC happy. We’ll also look into some similar materials and alternatives, including thermal pads, thermal grease, and even thermal potting compounds.
What is Thermal Compound?
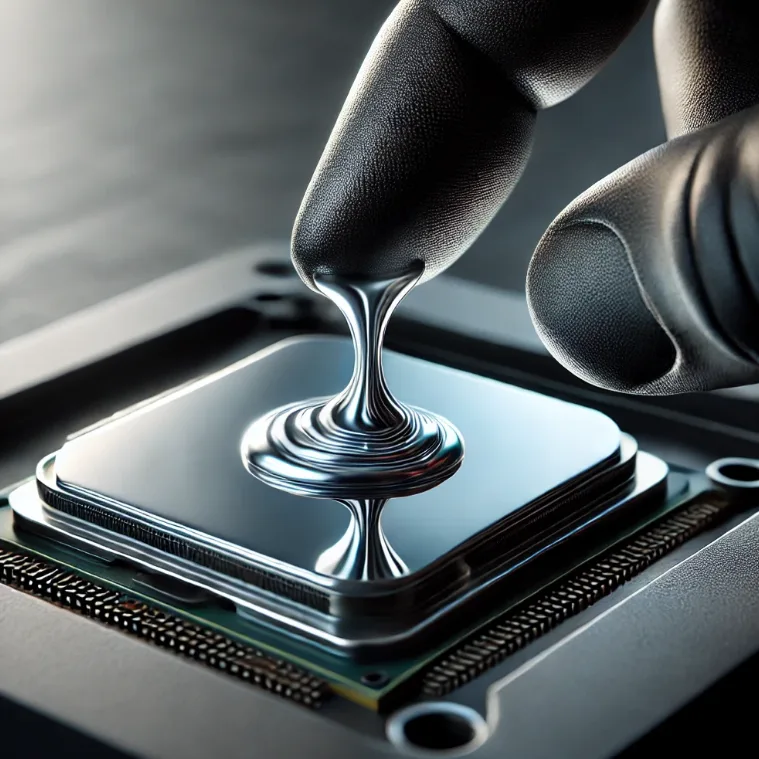
Thermal compound, also known as thermal paste or thermal grease, is a material applied between two surfaces to enhance heat conductivity. It’s the unsung hero standing between your overheating CPU and efficient cooling. But it’s not only for PCs—thermal compound can be found in telecom equipment, data centers, and even LED lights.
What is Thermal Compound Made Of?
The magic behind thermal compound comes from its components. Typically, thermal compounds are made of a base material, often silicone or a synthetic polymer, mixed with conductive fillers such as metal oxides, ceramics, or even silver. A thermal compound with a higher metal content—like aluminum or silver—tends to have better thermal conductivity. But watch out—using more metal may also make it electrically conductive, which is not ideal in all situations.

The differences in conductivity often boil down to these fillers. High-quality thermal compounds can achieve conductivity ratings of up to 13 W/mK (Watts per meter per Kelvin), according to an industry report by Thermal Management Monthly, whereas standard compounds tend to hover around 5 W/mK.
Thermal Compound vs Thermal Paste
Now, are thermal compound and thermal paste the same thing? Well, technically, yes. But while thermal paste is often used in the PC space, thermal compound is the broader term for similar materials used in a wide range of applications—from consumer electronics to telecom systems.
Thermal Compound vs Thermal Pad
Thermal pads are the convenient cousin of thermal compounds. They are solid materials, easy to apply, but often less efficient than thermal compounds because they can leave small air gaps that reduce thermal conductivity. A thermal compound, when properly applied, ensures almost no gap remains.
How Does Thermal Compound Work?
Thermal compound works by filling the microscopic imperfections between two surfaces, like a CPU and a heatsink. These imperfections, without a good thermal interface material, would trap air, which is a poor conductor of heat.
The Mechanism of Thermal Compound
When applied, the thermal compound fills in these imperfections and ensures an even heat transfer between surfaces. A layer that’s too thick may actually trap heat—which is why applying the right amount matters. Tests by Alexandria Engineering Journal found that using more than 1mm of thermal compound can reduce cooling efficiency by up to 30%.
Is Thermal Compound Conductive?
Most thermal compounds are not electrically conductive, which is an advantage. However, certain high-performance versions containing metal can be conductive, which means they must be used carefully to avoid short-circuiting components. When in doubt, always check the manufacturer’s instructions.
To learn how to properly apply thermal compound, please read: how to use thermal paste?
What is Thermal Potting Compound?
Thermal potting compounds are an advanced cousin of thermal paste. Unlike thermal paste, they are used to encapsulate electronic components, offering both heat management and environmental protection. This makes them popular in automotive electronics and other challenging environments where vibrations and temperature extremes are common.
What Are the Alternatives to Thermal Compound?
When thermal compound isn’t the right fit, other options step in to ensure effective heat management in electronic components.
Thermal Pad
Thermal pads are convenient, pre-formed alternatives that simplify the application process. While they offer slightly reduced thermal conductivity compared to compounds, their ease of use makes them ideal for mass production and applications requiring quick assembly.
Thermal Gel
Thermal gel is often utilized in mass-production settings due to its ease of automation and consistent application. This medium provides reliable heat transfer while accommodating minor imperfections in component surfaces, enhancing overall thermal performance.
Thermal Grease
Almost identical to thermal paste, thermal grease has a slightly lower viscosity, allowing it to spread more easily across surfaces. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications where a smooth, even layer is essential for optimal heat conduction.
Thermal Interface Phase Change Material
Thermal Interface Phase Change Materials are solid at room temperature but melt upon heating to improve interface conductivity. This property ensures that the material conforms perfectly to the surfaces, enhancing thermal transfer when the device is in operation.
Gap Filler
Gap fillers are soft, pliable materials designed to bridge spaces where components don’t perfectly align. They not only aid in heat dissipation but also provide mechanical stability, making them ideal for irregularly shaped or assembled electronic parts.
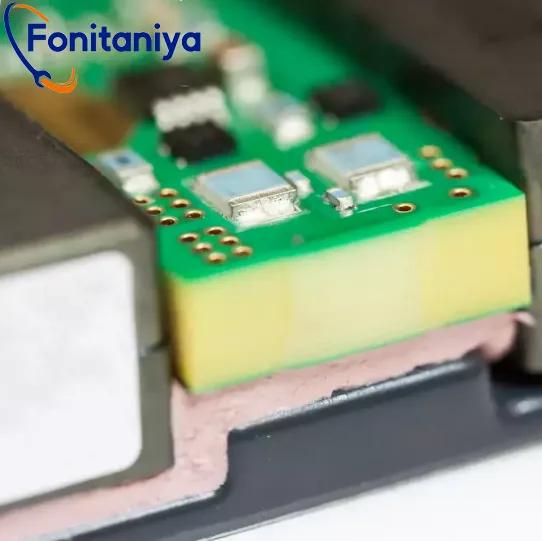
What is Thermal Wave-Absorber?
Thermal wave-absorbers are used in high-frequency environments, such as in telecom or radar systems, to mitigate heat buildup from electromagnetic waves. Imagine a specialized heat sponge—it soaks up the thermal energy and disperses it efficiently, reducing the risk of overheating. They play a crucial role in communication devices to keep them running smoothly.
Conclusion
Thermal compounds are more than just a handy material for cooling your PC—they’re the backbone of modern thermal management in countless applications. From data centers to telecommunications, they are crucial in keeping our devices running smoothly. Fonitaniya thermal adhesive company offers a wide range of thermal solutions, including thermal paste, thermal pads, and other thermal interface materials. We’re committed to helping you stay cool, no matter how hot things get.
FAQs
What is thermal compound used for?
Thermal compound is used to improve the heat transfer between surfaces, typically between a heat-generating component and a heatsink.
How often should you replace thermal compound?
It’s recommended to replace thermal compound every 2-3 years for PCs. Other devices may have different intervals based on usage and environment.
Is thermal compound better than a thermal pad?
Yes, thermal compound generally offers better heat transfer than thermal pads due to its ability to fill gaps more effectively.
Can I use too much thermal compound?
Yes, using too much thermal compound can trap heat rather than help dissipate it. A thin, even layer is best.
Is thermal compound necessary for my CPU?
Yes, a thermal compound is essential for proper heat dissipation between your CPU and heatsink. Without it, overheating could occur.
Do CPUs come with thermal compound?
If you purchase an assembled PC, CPUs should be with covered by thermal compound.