Understanding of a Chest Seal
Chest seals are critical medical interventions used primarily to manage open pneumothorax, commonly resulting from traumatic injuries like gunshot wounds, stabbings, or other penetrative chest traumas. Their primary purpose is to prevent air from entering the pleural cavity while allowing any trapped air or fluid to escape, thereby preventing the lung from collapsing—a condition potentially fatal if not managed promptly.
Purpose of Chest Seal
A chest seal is a specialized medical device designed to close wounds in the chest that might lead to pneumothorax. It serves as an emergency solution to keep the affected lung operational until further medical care can be provided. The primary role of these seals is to create an airtight occlusion over the wound, which stops outside air from entering the thoracic cavity and allows the lung to re-inflate or remain inflated.
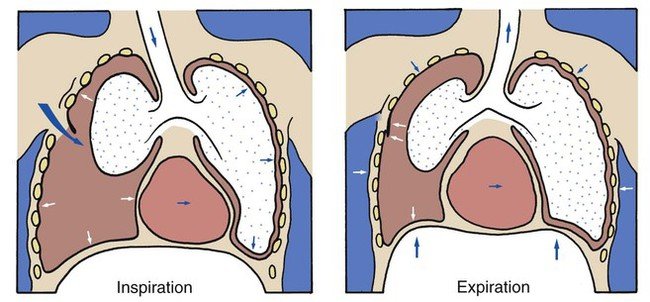
Chest seals are for preventing open-wound-induced pneumothorax, which could be fatal.
Material Specifications
Chest seals are typically constructed from thick, flexible materials that can conform to the body and maintain a strong adhesive bond despite the presence of blood, sweat, or dirt. Materials such as hydrocolloids or silicone-based compounds are often used for their skin-friendly properties and effective sealing capabilities.
The adhesive must be strong enough to adhere to wet skin and withstand external pressures during patient transport. Advances in hydrogel technologies have improved the overall performance of these adhesives, ensuring that the seal remains intact and effective over prolonged periods.
For business owners and procurement professionals, please learn more about the comparison of all popular brand here: A Business Intro: The Best Chest Seal.
Vented vs. Non-Vented Chest Seals
Vented Chest Seals
Vented chest seals are designed with a one-way valve that allows air to escape from the pleural cavity without letting any air enter. This feature is to prevent the development of a tension pneumothorax in an open chest wound. Vented seals are particularly beneficial in environments where immediate medical follow-up is delayed, and they are commonly used by military and emergency medical personnel.
Non-Vented Chest Seals
Non-vented chest seals, on the other hand, are used when the risk of developing a tension pneumothorax is low or when the air leakage is minimal. They create a completely occlusive environment that prevents any air from entering or escaping from the wound site. Non-vented seals are simpler in design and typically easier to apply, making them suitable for first aid scenarios by civilians or less trained individuals.
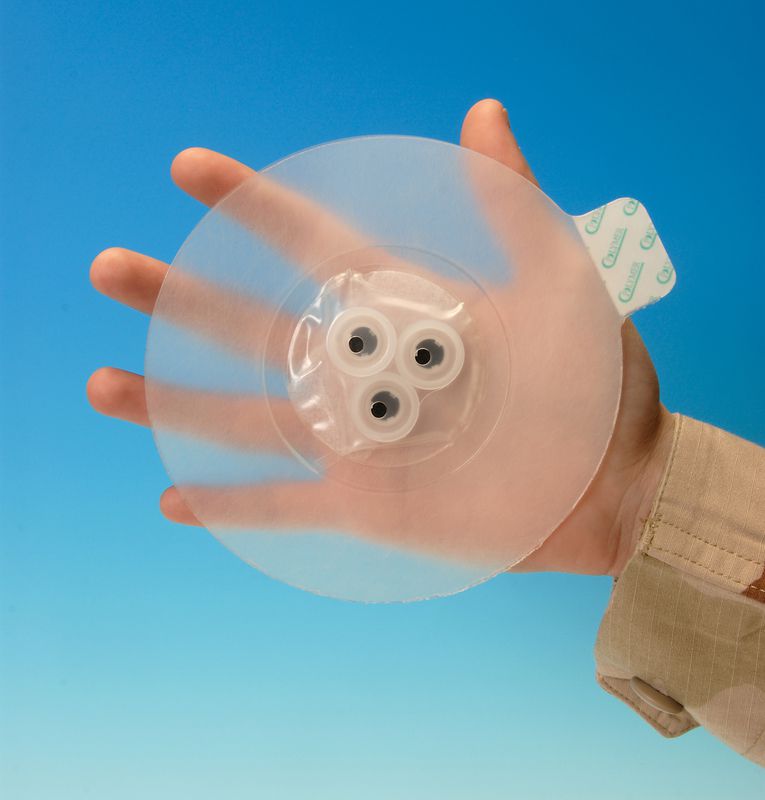
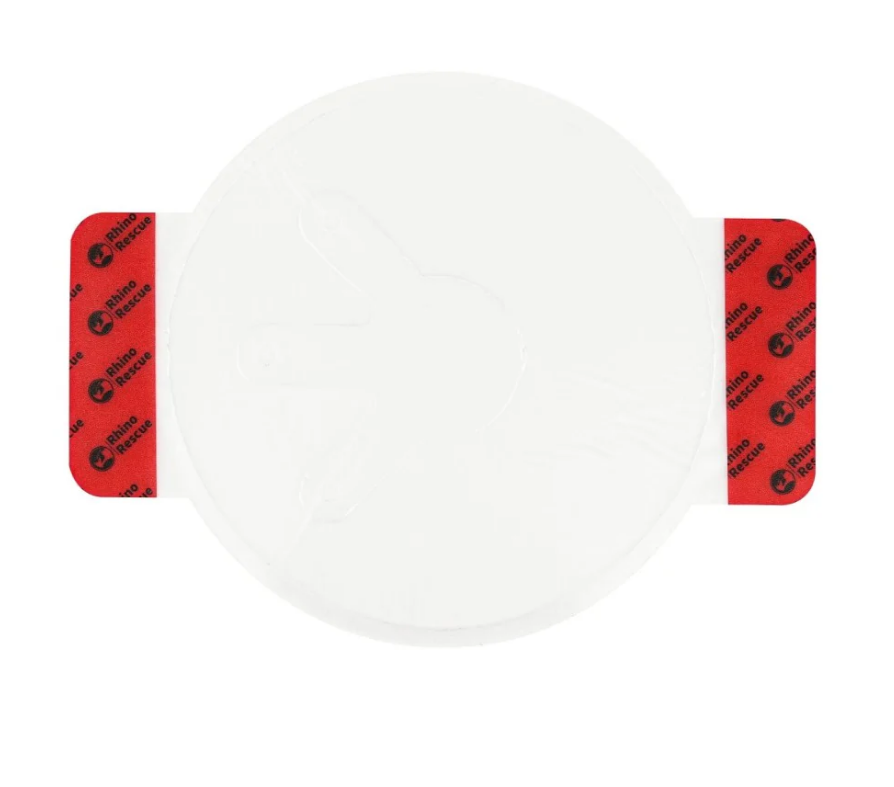


Vented chest seal vs non-vented chest seal
Choosing the Right Type for Different Situations
The choice between a vented and non-vented chest seal often depends on the specific medical situation and the environment in which the chest injury occurs. Vented seals are essential in cases of significant air leakage, while non-vented seals can be effective for managing less severe injuries.
Comparison of Effectiveness
Studies and clinical experience show that vented chest seals significantly reduce the risk of tension pneumothorax complications compared to non-vented seals, especially in severe trauma cases. It is crucial for first responders and medical providers to assess the wound and choose the appropriate type of seal based on the injury’s specifics and available resources.
At Fonitaniya™, we offer both vented chest seal and non-vented chest seal with high quality adhesives to meet multiple needs. Please click in the link: Fonitaniya™ First-Aid Chest Seal
What If No Chest Seals in Emergency Trauma Care?
Traditional first aid techniques for such injuries are limited and often insufficient to prevent the complications associated with open pneumothorax.
Traditional Management of Open Chest Wounds
Before the invention of chest seals, first responders relied on makeshift methods such as taping plastic sheets over wounds or using bandages, which often failed to prevent the ingress of air into the pleural cavity effectively. These methods, while rudimentary, were only marginally effective at maintaining the pulmonary function and could not adequately prevent pneumothorax, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Comparative Effectiveness of Chest Seals
Studies indicate that the application of chest seals significantly enhances survival rates in patients with traumatic pneumothorax compared to traditional methods. For example, a study published in the Journal of Emergency Medicine shows that the use of vented chest seals reduces the risk of tension pneumothorax by up to 70% compared to improvised solutions. The study further noted that survival rates improved from 51% to 83% with the use of commercially produced chest seals in pre-hospital settings.
Case Studies Highlighting the Impact of Chest Seals
Several case studies underscore the life-saving impact of chest seals in emergency care. In military conflicts, where chest injuries are prevalent, data gathered from battlefield medic reports reveal that the timely application of a chest seal reduced the incidence of cardiopulmonary arrest associated with chest wounds by over 60%. These case studies provide practical insights into the vital role that well-engineered chest seals play in enhancing the outcomes of traumatic chest injuries.
Clinical Applications of Chest Seals
Chest seals are indispensable in various emergency settings, from military combat zones to urban trauma incidents, reflecting their critical role in saving lives by managing chest wounds effectively.
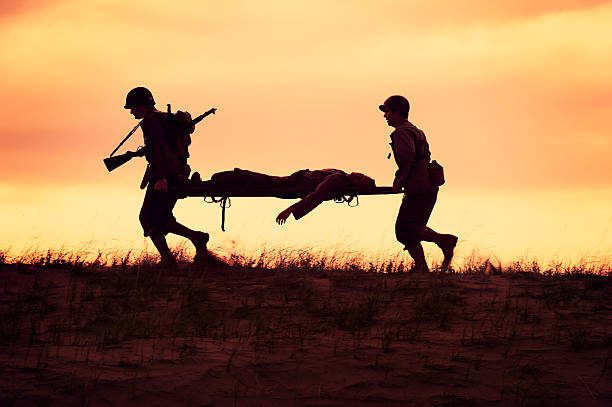

Chest Seals are mainly for military applications.
Emergency Use Scenarios
In the context of traumatic injuries, quick application of a chest seal can be life-saving. Emergency responders and military medics often use these devices in the field as part of their standard trauma management protocols, especially in cases involving chest penetrations where the risk of pneumothorax is high.
Benefits in Trauma Management
The timely use of a chest seal significantly reduces the mortality rates associated with traumatic chest injuries. By sealing the wound rapidly, it helps maintain adequate lung volume and oxygenation, which are vital in preventing the onset of shock and other complications resulting from major trauma.

To see other high-quality medical adhesiveness, please visit: medical products .
Potential for New Applications and Improvements
The future of chest seal technology may include smart chest seals equipped with sensors to monitor wound status, providing real-time data to healthcare professionals. This could lead to faster response times and more tailored treatment strategies, potentially integrating with telemedicine services. Innovations may also expand applications beyond trauma care into post-surgical recovery and chronic wound management, offering new market opportunities and enhancing patient care.
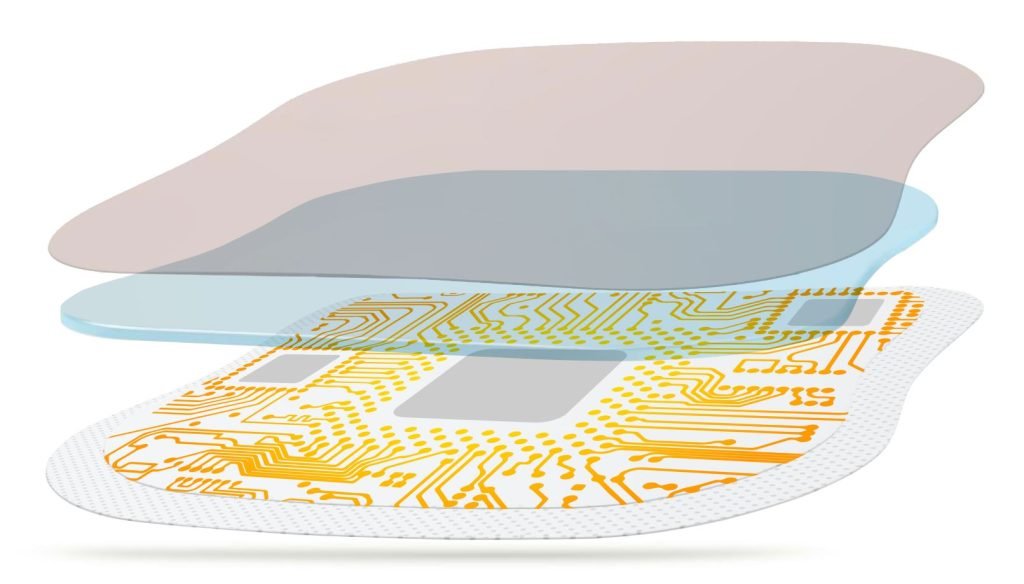
Integrating wearable technology into chest seal to monitor real-time condition of patient is the trending of future materials.
Conclusion
Chest seals are a key component in trauma management, offering immediate and potentially lifesaving intervention for pneumothorax induced by chest wounds. Their ability to prevent air from entering the pleural space while allowing air to escape can be the difference between life and death in emergency scenarios. The importance of chest seals in medical kits is underscored by their widespread adoption in military, emergency, and civilian trauma care.

Advances in Chest Seal Designs
At Fonitaniya, we continue to push the boundaries of medical device innovation. Our latest advancements in chest seal technology focus on enhancing the seal’s effectiveness in extreme conditions and improving user ease. With ongoing research and development, we aim to introduce next-generation chest seals that incorporate smart technologies for better wound monitoring and patient outcomes.
FAQs
How does a chest seal work to save lives?
Chest seals function by preventing air from entering the chest cavity while allowing trapped air and fluid to escape, which is crucial in treating pneumothorax.
Can you apply a chest seal to a sweaty or wet chest?
Yes, modern chest seals are designed to adhere well even on sweaty or slightly wet skin, though drying the area first is ideal for optimal adhesion.
What should you do if the chest wound continues to leak after applying a chest seal?
If leakage persists, check the seal’s edges for gaps, apply additional pressure, and be prepared to replace the seal if the problem continues.
How often should a chest seal be checked once applied?
You should check the seal regularly to ensure it remains airtight and adjust if necessary, especially if the patient’s condition changes.



